
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: hydrocarbon that are composed of multiple aromatic rings. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C 6H 6. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. Also called cycloolefin.Īromatic hydrocarbon: A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms.
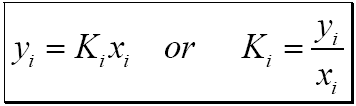
Also called naphthene.Ĭycloalkene: An alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed ring of carbon atoms, but has no aromatic character, with the general formula C nH 2n-2. Also called acetylene.Ĭycloalkane: A one-ring (monocyclic) saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C nH 2n. Also called olefine.Īlkyne: An unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond, with the general formula C nH 2n-2. Also called paraffin.Īlkene: An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond, with the general formula C nH 2n. Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.Īlkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C nH 2n+2.
#Depriester chart in bar calculator full
See also pKa values for phenols, alcohols and carboxylic acids.įor full table - rotate the screen! Boiling point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16☌īoiling point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16, ☏ See also Melting points of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, densities for different kinds of organic compounds and density, boiling and melting points of nitrogen and sulfur compounds. Multisubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkene < normal alkene < normal alkane < alkyl cyclohexane < alkylbenzene < cycloalkene < cycloalkane < 2-, 4- and 3-alkanol / 1-alkylnaphthalene < 1-alkanol < normal alkanoic acidįor melting points, the trends are more varying with increasing carbon number for the different types of hydrocarbons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
